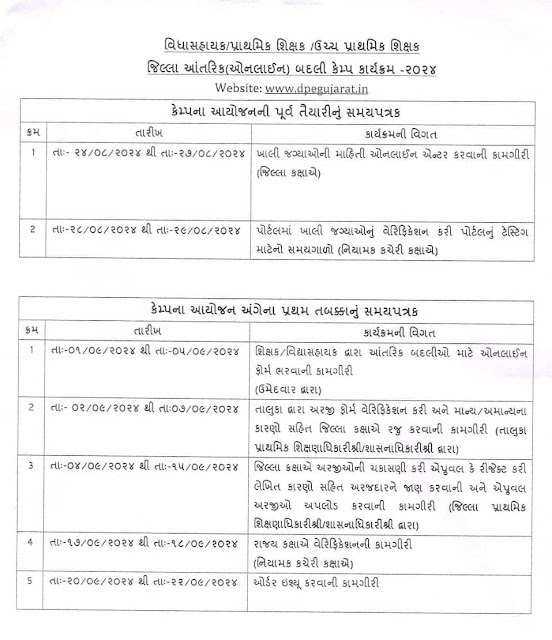
NPS KHATA MATHI UPAD MATE NO HUKAM NO NAMUNO SEE HERE
The National Pension System (NPS) is a voluntary defined contribution pension system administered and regulated by the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority(PFRDA), created by an Act of the Parliament of India. The NPS started with the decision of the Government of India to stop defined benefit pensions for all its employees who joined after 1 January 2004. While the scheme was initially designed for government employees only, it was opened up for all citizens of India in 2009. NPS is an attempt by the government to create a pensioned society in India. In its overall structure NPS is closer to 401(k) plans of the United States. Today, the NPS[12] is readily available and tax efficient under Section 80CCC and Section 80CCD. Under the NPS, an individual can contribute to his retirement account. Also, his employer can contribute to the welfare and social security of the individual.
NPS is a quasi-EET instrument in India where 40% of the corpus escapes tax at maturity, while 60% of the corpus is taxable.[13][14][15] Of the 60% taxable corpus, 40% is tax-exempt as it has to be compulsorily used to purchase an annuity.[16] The annuity income will be taxed, though. The remaining 20% alone will now be taxed at slab rates on withdrawal.[17]NPS offers subscribers a choice of two record keeping agencies: NCRA (NSDL-CRA) and KCRA (Karvy-CRA).[18][19] In 2017 Union budget of India, 25% exemption of the contribution made by an employee has been announced as a form of premature partial withdrawal in NPS.[20] This amendment will take effect on 1 April, 2018 and will, accordingly, apply in relation to the assessment year 2018-19.[21][22] NPS is a market-linked annuity product.[23]